The Future of Syria Between Discentralism and Division
Since the beginning of the formation of the Syrian state, it has been ruled by many regimes, and they were all pluralistic regimes with a truly democratic orientation. However, they were subjected to repeated coups, until the totalitarian Baath Party, with its extremist and fascist orientation in every sense of the word, came to power. The Assad family ruled the Baath state for more than half a century. During that period, the Syrian people experienced all kinds of oppression and persecution under the dominance of a hateful dictatorial rule. In the first stage, all the leaders and founders of the Baath Party were liquidated and replaced by a gang of criminals and bandits who wreaked havoc in the body of the Syrian state and wove the threads of dictatorship in a tight manner; until the Syrian people thought that their reality had become a given and Unchangeable.
The Secular orientation and fight against Salafist thought in Syria:
After the Baath Party took power in Syria, it began its first steps towards consolidating the pillars of its rule; through what was then called the Corrective Movement on November 16, 1970. The party adopted its secular leftist direction and linked up with the socialist camp to clash with the Salafi Brotherhood ideology that began to spread in the Middle East at that time, and in Syria since 1940. The security branches and intelligence took over the rule in Syria, and everyone who approached religion was arrested and thrown into prison. Mosque preachers were also directed to glorify the Baathist regime and pray for it, as it was not permissible for anyone to criticize the ruler or the party, and intelligence spread throughout the Syrian state. The slogan “There is no God except the homeland and no messenger except resurrection” was raised. The Hama events were 1976-1982 was the decisive period in suppressing and curbing the Brotherhood rebellion, as the Defense Brigades, led by Rifaat al-Assad, the brother of the late President Hafez al-Assad, the 47th Tank Brigade, the 21st Mechanized Brigade, and the 21st Airborne Regiment (Special Forces) intervened. This operation came in response to the assassination attempt on President Hafez al-Assad on June 26, 1980, when he received the President of Mali. The party committed horrific massacres against the residents of Hama, killing more than thirty thousand people. As for the rest, they became wanted, some of whom died In the prisons of the Baath regime and they remained detained until the fall of the Baath regime at the hands of the Salafist Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) on December 8, 2024. For the first time, the contents of the prisons were revealed and secret prisons were found that no one had known about before.
Building the alleged steadfastness and confrontation front and establishing the resistance axis:
In order for the Baath regime to complete its project of controlling all aspects of the Syrian state joined what was called the Steadfastness and Confrontation Front, which was called for by the late Libyan President Muammar Gaddafi in November 1977. It was an alliance that included Libya, Algeria, Syria, Iraq, the Palestine Liberation Organization, and the People’s Democratic Republic of Yemen. The Front was a response to the Camp David Accords concluded by the former Egyptian President Mohamed Anwar Sadat with Israel with American mediation. These countries tried to isolate the Egyptian Republic from the Arab League, but the Front quickly dissolved after the outbreak of the Iran – Iraq War in 1980. Relations between Syria and Iraq deteriorated after that war, and Syria joined the “Axis of Resistance” that began in Iran, passing through Syria to Lebanon, where the Syrian army had invaded Lebanon under the pretext of stopping the civil war there. “Hezbollah” represents the axis in Lebanon, and in Yemen it is represented by the “Houthis”, and in Iraq by the “Popular Mobilization”, and in Palestine the “Hamas and Islamic Jihad” movements.
With the beginning of the Gaza War on October 7, 2023, the axis of resistance was subjected to major blows, as most of the leaders of Hezbollah and Hamas were eliminated, followed by the overthrow of the Assad regime in Syria on December 8, 2024.
The Syrian movement and joining the so-called Arab Spring revolutions:
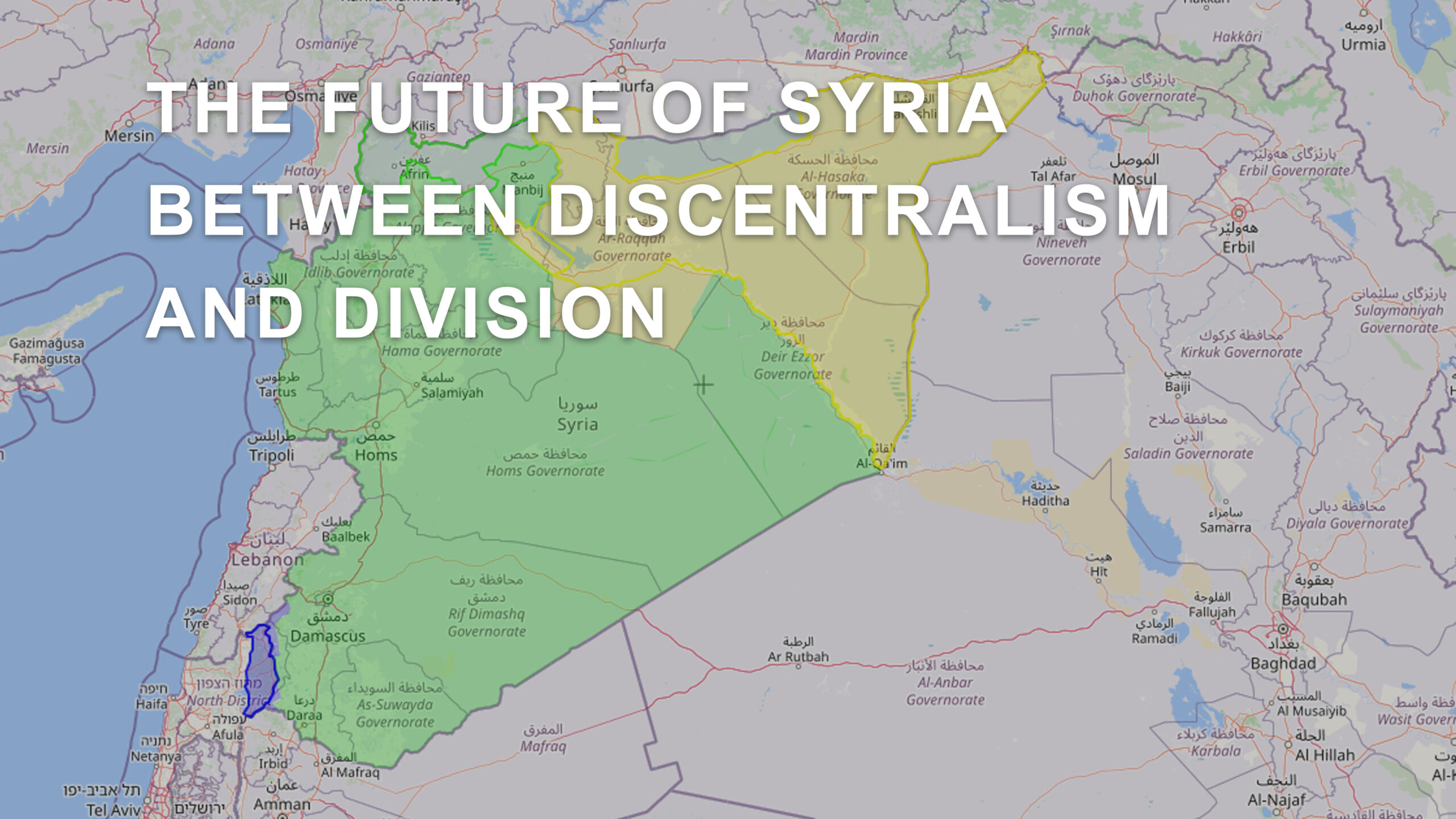
The Syrian people started with their peaceful revolution on March 15, 2011. It was a peaceful revolution calling for amending some articles of the Syrian constitution, releasing freedoms, and removing martial law. However, the Syrian Baathist regime responded with armed violence. The Turkish state, led by Erdogan and the Justice and Development government, provided military, media, and logistical support. The Syrian revolution began to be militarized and diverted from its peaceful path. As a result of the conflicting interests of regional and international countries regarding the fate of the Syrian people, the duration of the Syrian movement was prolonged, and Syria was exposed, during it, to all kinds of interventions. Many regional and international parties and powers intervened in the Syrian arena, where people were displaced and immigrated. More than half of Syria’s population, Iran, Hezbollah, and Russia intervened at the invitation of the Syrian government, as did America and the international coalition forces after the emergence of the terrorist organization ISIS, which was confronted by the People’s Protection Units, the Women’s Protection Units, and then the Syrian Democratic Forces, which eliminated it and destroyed its alleged capital in Raqqa. As for Turkey, as a result of its historical ambitions in the region, it intervened through its mercenaries at first, and at a later stage it intervened directly to occupy large areas of Syrian geography; all this scene foreshadowed an unstable future for the Syrian state under the dominance of the Baath regime, and the will of the Syrian people and all their legitimate rights to self-determination and confront the attempts of regional and international powers to fragment the Syrian fabric and divide Syrian geography according to their agendas and the interests of regional countries were taken away.
Scenarios awaiting the future of Syria if the popular base does not take the initiative:
Most of the data that was mentioned before lead to two outcomes if the popular groups in Syria do not seek to take the initiative and lead the transitional process in Syria:
The first scenario: is to return Syria to the point of no solution and establish a centralized, totalitarian regime with clear religious and sectarian tendencies and orientations; and naturally it will clash with the popular masses in Syria in particular, due to the scientific and technological progress that the world has achieved, the diversity of social media, and the liberal freedoms that have invaded most societies, including conservative societies as well.
The other scenario: It is consistent with the Greater Middle East project – the new one, which -is the project of partition and changing the political map of the Syrian state and fragmenting it into several states that differ in ethnic, religious and sectarian fields, but this scenario also does not serve the orientations of the Syrian elite; as Syria has been distinguished and advanced by its ethnic, religious and sectarian diversity ; and such a scenario will fragment the integrated Syrian society, and lead the region to future conflicts with disastrous results and dire consequences for nationalities and sects.
solution of the democratic nation and Autonomous-administration of Syria instead of centralization and division:
There is no doubt that the Syrian social fabric is a highly diverse fabric, and regional countries and powers have greatly influenced its structure. This has led to sectarian and religious diversity and the emergence of fanaticism in this context. Iran and its arms in the region feed the fanaticism of the Alawite sect, and the Sunnis are controlled by Turkey, Al-Azhar, and the extremist ideology of the Brotherhood, in addition to some Gulf countries. The Christian sect, with its different sects, receives support and endorsement from the international Christian community (each according to its affiliation). As for the Kurdish people, they undoubtedly pay the price of the differences between those sects and ethnicities, and all spectrums of Syrian society treat them with marginalization, denial, and exclusion. If we analyze Syrian development with a realistic scientific perspective and take into consideration the mosaic diversity of Syria throughout the history of contemporary Syria, we will find that there must be an integrated system capable of managing Syria with its various spectrums and achieving social justice. The answer to the current global development (globalization) must be a system that guarantees the legitimate rights of all the people of Syria and respects their free will, and is highly sensitive to the pragmatic intellectual orientations of the Syrian people. At the same time, it defends stability and security inside and outside the Syrian geography, and that system will only exist in the paradigm of the democratic nation and the system of democratic Autonomous-administration, as the totalitarian central system has proven its ineffectiveness; and has led Syria to intellectual and moral destruction and the collapse of the body of the Syrian state.
The idea of division on sectarian grounds is also no less dangerous than centralization, and therefore, as we mentioned at the beginning, the solution of decentralization and federal union – similar to many countries (America, Russia, France, Switzerland, the Emirates… and many others) that have a significant weight and role in the global balance of power – is the ideal solution for the new Syria, and it is the one that will contain the clear disparity in the Syrian national fabric.




